Implementing Linked Lists In JavaScript
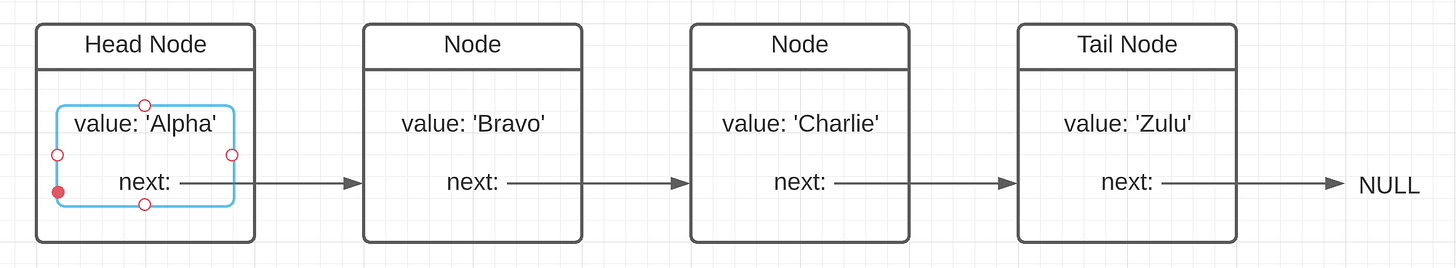
A null-terminated singly-linked list
A linked list is a linear data structure where each node gets stored at unordered locations in memory. The first node in a linked list is the head and the last node is the tail. A node in a linked list will contain at least a value to store and a pointer to the next node. A pointer is a reference to an object. Linked lists are either singly-linked or doubly-linked. A node in a doubly-linked list has an extra pointer to the previous node. This means you can traverse the list in both forward and backward directions at the cost of using up more space for the extra pointer. Linked lists can either be circular (the tail node points to the head) or null-terminated (the tail node points to null).
In a linked list, the time complexity for an element lookup is O(n) as we have to traverse the list from the head until we find the element. In comparison, an array has an O(1) time complexity for looking up an element. Another advantage an array has over a linked list is that most computers read data from sequential memory faster than non-contiguous memory. Inserting and deleting in a linked list would be faster than in an array because there is no need to shift the elements after the operation. Here are links to the implementation of a singly-linked list and doubly-linked list with JavaScript.
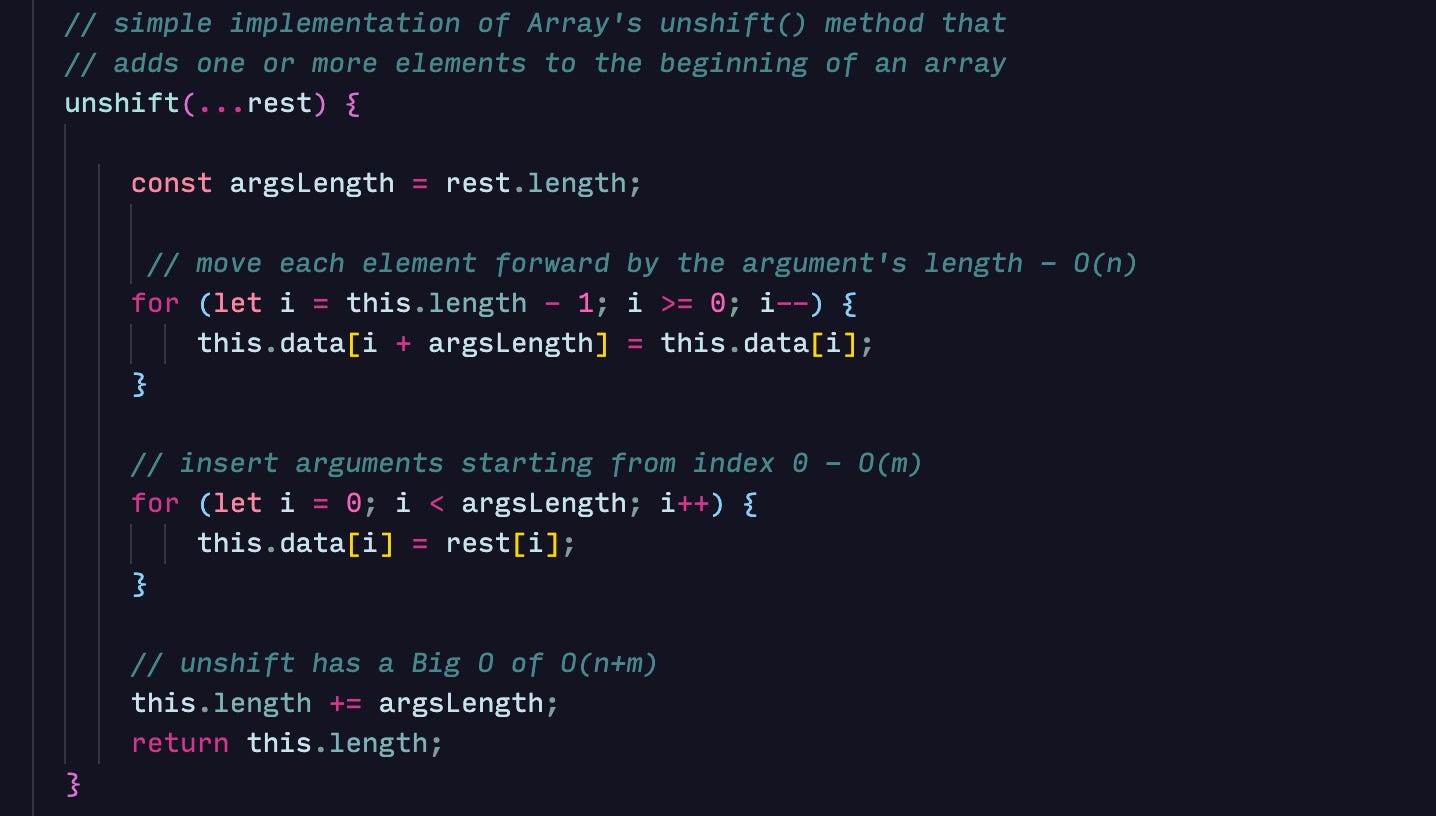
Inserting one or more elements at the beginning of an array
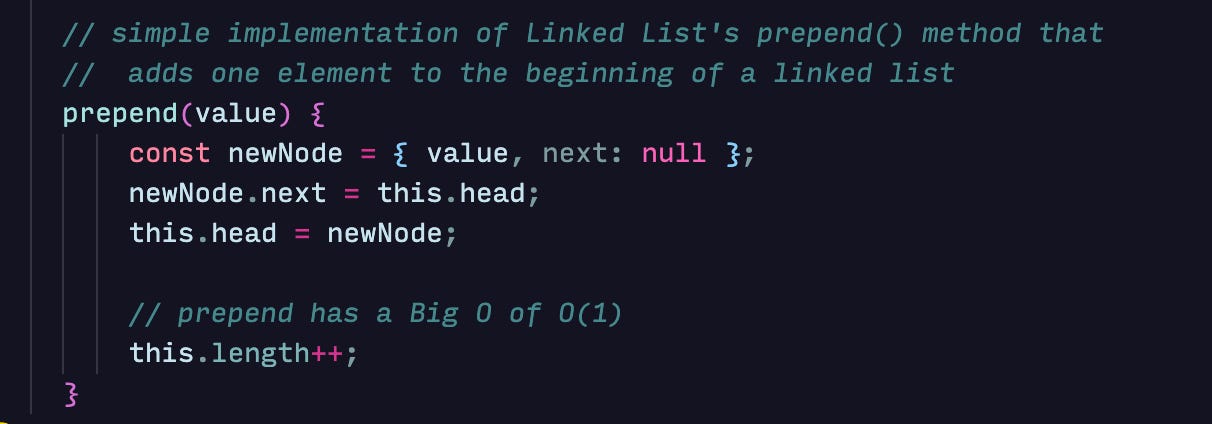
Prepending an element to a linked list
A common interview question is implementing a method to reverse a linked list. To do this, we can traverse the linked list from the second element and reverse the next pointer of each node to reference the value preceding the node.
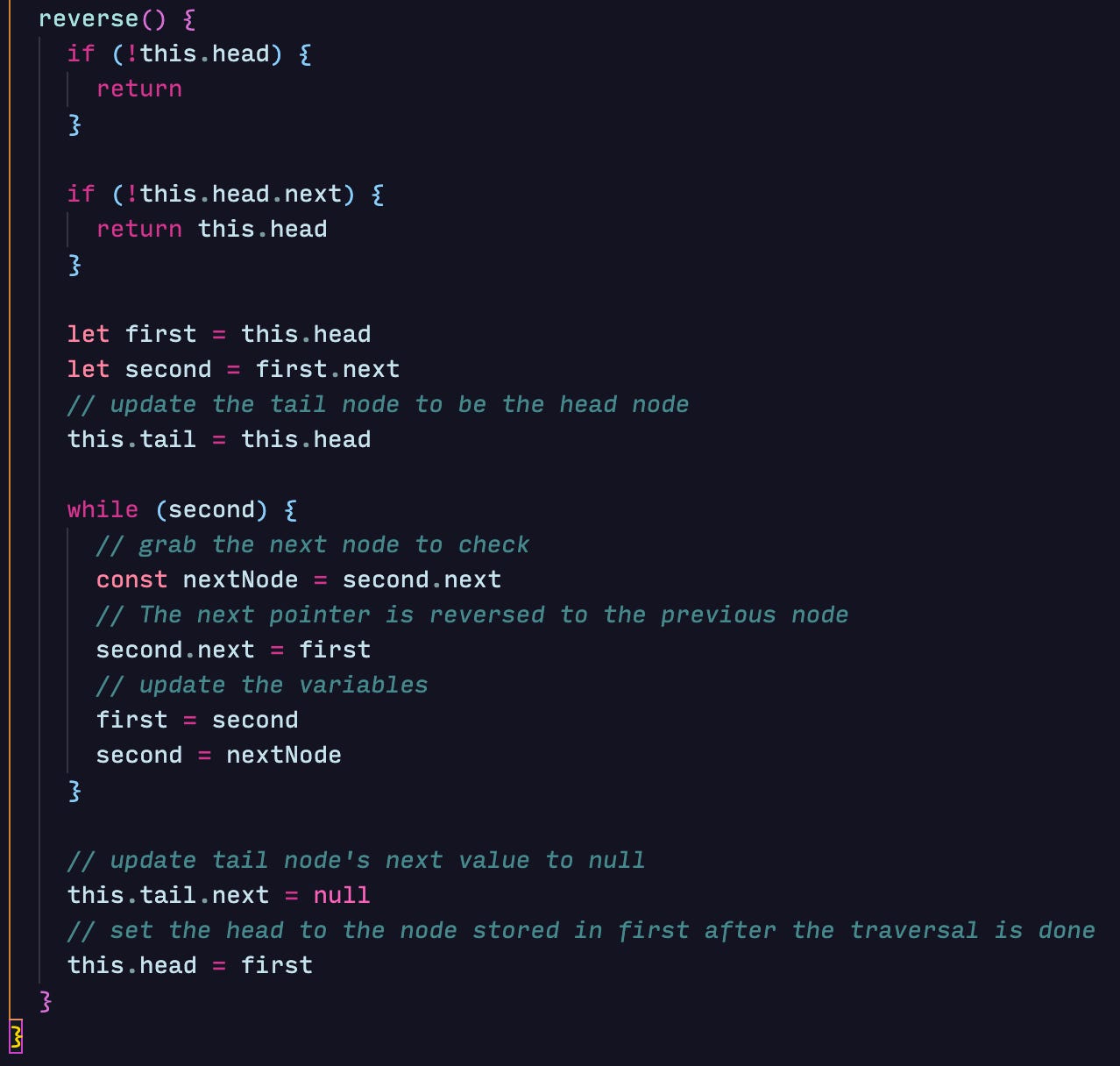
Reversing a linked list
We also have to update the tail node to hold the value currently in the head node and set its next pointer to null. When the loop finishes, the first variable will hold the last node in the linked list with an updated next pointer — the node before it instead of null. This variable will become the new head node.
Linked lists are a low-level data structure that can be used in building higher-level data structures like stacks and queues (I’ll write a post on these two shortly). I hope this helps.
